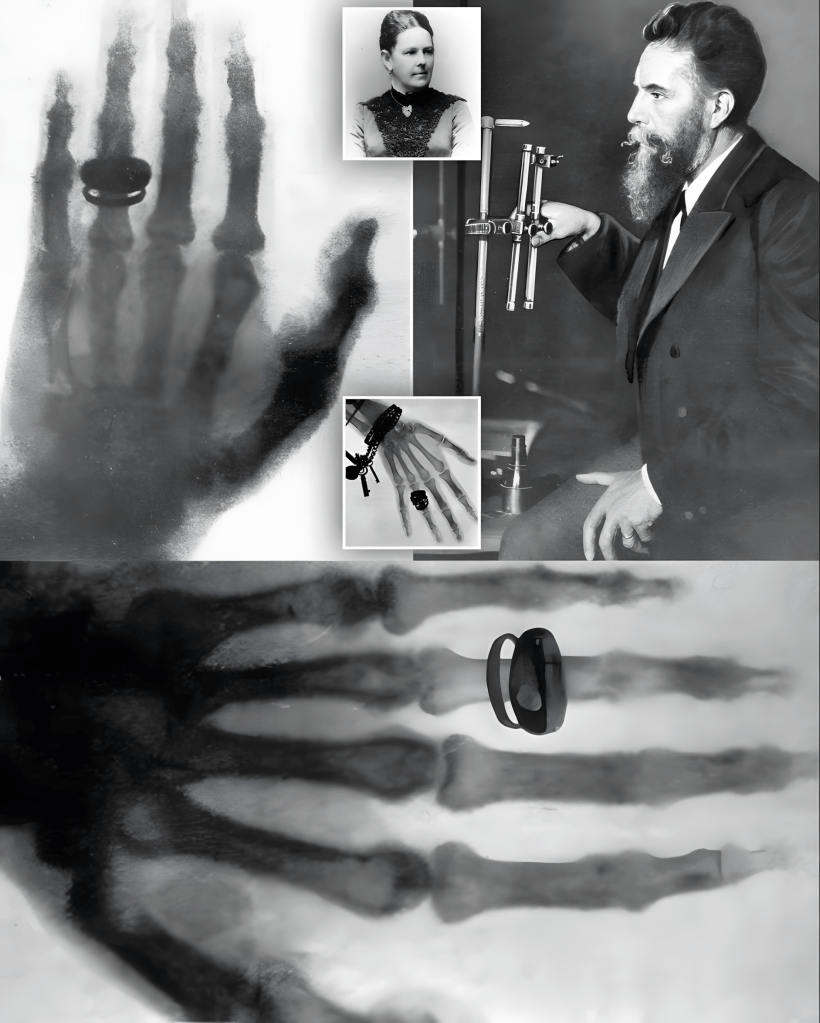
1895년, 독일 물리학자 빌헬름 콘라트 뢴트겐Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen이 음극선관cathode-ray tubes 실험 중 엑스선X-rays을 발견했다.
근접 촬영한 화면에서 나오는 빛을 보고, 그는 최초의 엑스선을 포착했다. 바로 아내의 손이었다.
이 엑스선은 수술 없이 신체 내부를 관찰할 수 있게 함으로써 의학 혁명을 불러왔다.
엑스선의 유용성은 즉시 인정되었지만, 방사선 위험은 알려지지 않았다.
뢴트겐은 1901년 최초의 노벨 물리학상을 수상했지만, 자신의 발명품에 대한 특허는 취득하지 않았다.
In 1895, German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered X-rays while experimenting with cathode-ray tubes. Noticing a glow coming from a close-up screen, he captured the first X-ray ever: his wife’s hand.
This revolutionized medicine by allowing you to observe the inside of the body without surgery. Although its usefulness was recognized immediately, the radiation risks were unknown.
Röntgen received the first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901 and never patented his invention.
댓글 남기기